当前困扰数值预报模式在短时临近降水预报(0-6h)中应用的一个突出问题是平衡调整(Spin-up)问题,平衡调整阶段中模式不能产生足够的上升运动,导致前几小时的预报无效,即使成熟的快速更新雷达资料同化也仍需要1-4小时的平衡调整时间。
闪电是强对流发展的产物,可有效指示雷暴云中的上升运动和冷云微物理过程。近年来,闪电探测和定位技术有了很大进步,从1970年代误差在公里到数公里的单站定位,到1980年代误差在几百米的地闪落地点定位,发展到目前误差仅有百米甚至米量级的多站闪电全闪放电通道的三维动态定位。闪电定位技术的发展,几乎使地球上任何地方发生的闪电都能被可靠探测。地基闪电定位资料质量不断提高的同时,基于静止卫星平台的闪电成像仪也已在轨运行。面对日渐丰富的闪电定位资料,如何进一步发挥闪电资料在模式中的应用价值,提高强对流和降水的预报水平成为临近预报研究的重要科学问题。
为获取可靠的闪电定位资料,并促进闪电在改进降水短临预报中的应用,大气所郄秀书团队自主发展了雷电全闪探测和三维定位系统(BLNET),并连续多年开展暖季综合观测实验,获得了北京及周边雷暴天气系统特征和规律的实际认识(Qie et al.,2021)。在充分研究闪电与对流系统动力、微物理过程联系的基础上(Chen et al.,2020a; Lu et al.,2021),陆续建立了闪电与冰物质含量(Qie et al.,2014)、水物质含量(Chen et al.,2019)等微物理特征的经验关系,发展了闪电资料在对流分辨模式中的牛顿松弛逼近(Nudging)同化方案。闪电资料同化可以在雷达资料基础上引入更多对流信息,提高局地降水短临预报的准确性。
最近,郄秀书团队和美国国家大气研究中心的Juanzhen Sun高级科学家、北京城市气象研究院的肖现博士(2017年大气所毕业)合作,基于闪电和云内强上升运动的物理联系,利用闪电和模式垂直速度经验廓线,提取对流尺度动力场观测信息,并在雷达四维变分同化系统VDRAS内实现了闪电资料的同化应用(Xiao et al. 2021a, b),有效改进了模式的动力场状态,提高了对流性降水定量预报的准确性,在精细化预报强降水中心的同时,也减少了空报范围。
目前搭载于我国FY-4静止气象卫星上的我国首个闪电成像仪LMI已实现了对东亚地区闪电活动的准实时连续监测。团队成员陈志雄博士在对LMI资料性能进行评估(Chen et al., 2021)的基础上,探索了基于LMI的闪电资料同化方法,开发了基于WRFDA三维变分同化系统的闪电资料同化方案(Chen et al. 2020b),进一步拓展了卫星观测资料和新同化方法的应用,有望在雷达稀少或不能观测区域(如海上和山区),利用具有独特优势的闪电观测资料提升强对流天气临近预报的准确性。
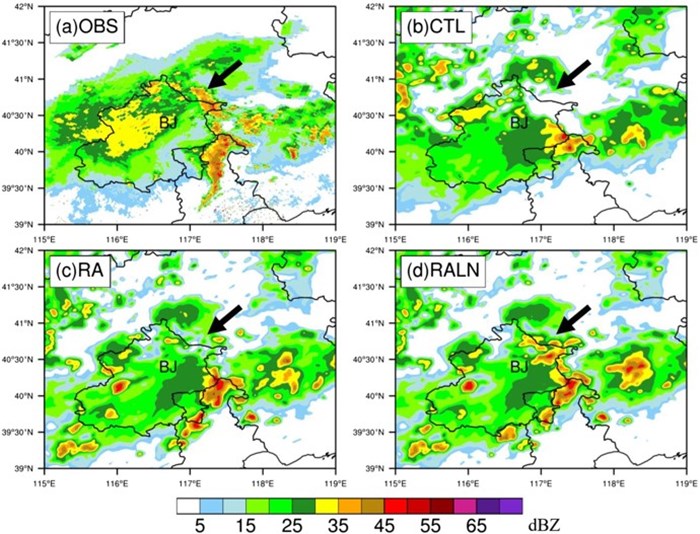
图 基于WRFDA三维变分同化系统的闪电资料同化提高局地降水预报准确性,预报时间为 2018年 7 月 16 日 05:00 (Chen et al., 2020b)。OBS为北京市气象局的雷达组合反射率产品;CTL未进行雷达和闪电同化模拟的组合反射率预报;(c)RA只同化雷达资料预报;(d)RALN同化雷达与闪电资料预报
References:
Qie X., Yuan S., Chen Z., et al., 2021: Understanding the dynamical–microphysical and lightning processes associated with severe thunderstorms over the Beijing metropolitan region. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(1):10–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9656-8
Xiao X., Sun J., Qie X., et al., 2021: Lightning data assimilation scheme in a 4DVAR system and its impact on very-short-term convective forecasting. Mon. Weather Rev., 149(2): 353-373. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-19-0396.1
Xiao X., Qie X., Chen Z., et al., 2021: Evaluating the performance of lightning data assimilation from BLNET observations in a 4DVAR-based weather nowcasting model for a high-impact weather over Beijing. Remote Sens., 13(11), 2084. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112084
Lu J., X. Qie, R. Jiang, et al., 2021: Convective cloud mergers and their impact on lightning activity in a severe squall-line system over the Beijing Metropolitan Region. Atmos. Res., 256, 105555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105555
Chen Z., Qie X., Sun J. et al., 2021: Evaluation of Fengyun-4A Lightning Mapping Imager (LMI) performance during multiple convective episodes over Beijing. Remote Sens., 13(9):1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091746
Chen Z., Qie X., Yair Y., et al., 2020a: Electrical evolution of a rapidly developing MCS during its vigorous vertical growth phase. Atmos. Res., doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105201.
Chen Z., Sun J., Qie X., et al., 2020b: A method to update model kinematic states by assimilating satellite‐observed total lightning data to improve convective analysis and forecasting. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 125, JD033330. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JD033330.
Chen, Z., Qie, X., Liu, D., & Xiong, Y. (2019). Lightning data assimilation with comprehensively nudging water contents at cloud‐resolvingscale using WRF model. Atmospheric Research, 22, 72–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.02.001
Qie, X., Zhu, R., Yuan, T., Wu, X., Li, W., & Liu, D. (2014). Application of total‐lightning data assimilation in a mesoscale convective system based on the WRF model. Atmospheric Research, 145, 255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.04.012






